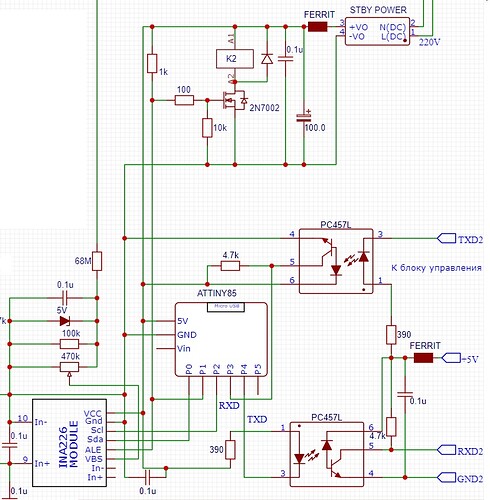
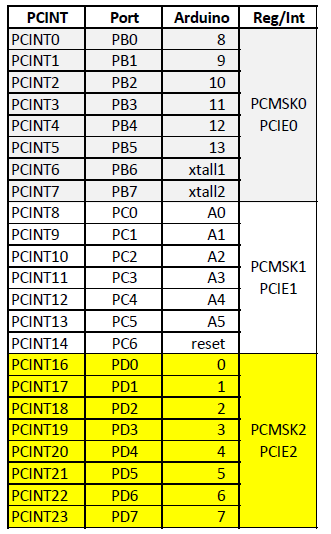
не знаю, может и неправильно, пробуй:
/***************************************************************************
* Example sketch for the INA226_WE library
*
* This sketch shows how to use the limit alert of the INA226 module.
*
* Further information can be found on:
* https://wolles-elektronikkiste.de/en/ina226-current-and-power-sensor (English)
* https://wolles-elektronikkiste.de/ina226 (German)
*
***************************************************************************/
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
SoftwareSerial mySerial(3, 4);
#include <Wire.h>
#include <INA226_WE.h>
#define I2C_ADDRESS 0x40
#include <EEPROM.h>
int interruptPin = 1;
volatile bool event = false;
INA226_WE ina226 = INA226_WE(I2C_ADDRESS);
//
const int INTERRUPT_PIN = PCINT1;
float Imax_mA = 500.0;
//
struct {
float busVoltage_V = 0.0;
float current_mA = 0.0;
float power_mW = 0.0;
byte alarm = 0;
byte crc;
} senddata;
struct TRXDATA {
byte cmd;
float Imax;
float ImaxOut;
byte crct;
};
//
void setup() {
EEPROM.get(4,Imax_mA); //читаем данные с 4 по 7 ячейки памяти значение сигнализации Imax
if ((isnanf(Imax_mA)==true)||((Imax_mA<300.0)||(Imax_mA>1000.0)))
{
EEPROM.put(4,500.0); EEPROM.get(4,Imax_mA);
}
//
mySerial.begin(19200);
mySerial.setTimeout(50);
Wire.begin();
ina226.setMeasureMode(CONTINUOUS);
ina226.init();
ina226.setAlertType(CURRENT_OVER, Imax_mA);
ina226.enableAlertLatch();
/** Setup Interrupts for ATtiny85 */
cli(); // clear any interrupts
// PCMSK |= (1 << INTERRUPT_PIN); // enable interrupts only on interrupt pin
// MCUCR |= (1 << 3); // configure only to trigger interrupts on rising edge
// GIMSK |= (1 << PCIE); // enable pin change interrupts
// GIMSK=1<<PCIE;
// PCMSK=1<<PCINT1;
GIMSK = 0b00100000; // turns on pin change interrupts
PCMSK = 0b00000010; // turn on interrupts on pin PB1
pinMode(INTERRUPT_PIN, INPUT); // has a physical pull up on breadboard
sei();
ina226.readAndClearFlags();
}
void saveImax(TRXDATA & t)
{
// save to eeprom
EEPROM.put(4,t.Imax);
ina226.setAlertType(CURRENT_OVER, t.Imax);
t.ImaxOut = t.Imax;
}
void loop() {
TRXDATA trxdata{};
byte crct;
if(event) {
ina226.readAndClearFlags(); // reads interrupt and overflow flags and deletes them
sendData();
//!!! attachInterrupt(digitalPinToInterrupt(interruptPin), alert, FALLING);
event = false;
ina226.readAndClearFlags();
} else {
byte* buf;
buf = (byte*)&trxdata;
mySerial.flush();
while (mySerial.available() > 0)
{
mySerial.readBytes((byte*)&trxdata, sizeof(trxdata));
}
switch (trxdata.cmd) {
case '@':
sendData();
break;
case '#':
trxdata.cmd = 'R';
trxdata.ImaxOut = trxdata.Imax;
crct = crc8((byte*)&trxdata, sizeof(trxdata) - 1);
trxdata.crct = crct;
mySerial.write((byte*)&trxdata,sizeof(trxdata));
saveImax(trxdata);
break;
case '$':
float Imax_E;
EEPROM.get(4,Imax_E);
mySerial.write((byte*)&Imax_E,sizeof(Imax_E));
break;
}
}
}
// End loop
//++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
//
void sendData() {
float shuntVoltage_mV = 0.0;
float loadVoltage_V = 0.0;
float busVoltage_V = 0.0;
float current_mA = 0.0;
float power_mW = 0.0;
shuntVoltage_mV = ina226.getShuntVoltage_mV();
senddata.busVoltage_V = (ina226.getBusVoltage_V() >= 0 ? ina226.getBusVoltage_V() : 0.0);
senddata.current_mA = (ina226.getCurrent_mA() >= 0 ? ina226.getCurrent_mA() : 0.0);
senddata.power_mW = (ina226.getBusPower() >= 0 ? ina226.getBusPower() : 0.0);
loadVoltage_V = busVoltage_V + (shuntVoltage_mV/1000);
if (event) senddata.alarm = 1;
else senddata.alarm = 0;
// расчёт CRC (без последнего байта)
byte crct = crc8((byte*)&senddata, sizeof(senddata) - 1);
// пакуем в посылку
senddata.crc = crct;
// mySerial.print(String('\3')+"PW"+String(power_mW)+" CU"+String(current_mA)+" VO"+String(busVoltage_V)+" AL"+String(Alert)+" "+String('\4'));
// mySerial.print(String('\3')+"PW"+String(power_mW)+" CU"+String(current_mA)+" VO"+String(busVoltage_V)+" "+String('\4'));
mySerial.write((byte*)&senddata,sizeof(senddata));
}
//
void alert(){
/* */
//ISR (PCINT0_vect) {
if (PINB&(1<<PINB1)) { return;}
event = true;
// detachInterrupt(1);
}
/* */
//
byte crc8(byte *buffer, byte size) {
byte crc = 0;
for (byte i = 0; i < size; i++) {
byte data = buffer[i];
for (int j = 8; j > 0; j--) {
crc = ((crc ^ data) & 1) ? (crc >> 1) ^ 0x8C : (crc >> 1);
data >>= 1;
}
}
return crc;
}
//
и файл SoftwareSerial.cpp
/*
SoftwareSerial.cpp (formerly NewSoftSerial.cpp) -
Multi-instance software serial library for Arduino/Wiring
-- Interrupt-driven receive and other improvements by ladyada
(http://ladyada.net)
-- Tuning, circular buffer, derivation from class Print/Stream,
multi-instance support, porting to 8MHz processors,
various optimizations, PROGMEM delay tables, inverse logic and
direct port writing by Mikal Hart (http://www.arduiniana.org)
-- Pin change interrupt macros by Paul Stoffregen (http://www.pjrc.com)
-- 20MHz processor support by Garrett Mace (http://www.macetech.com)
-- ATmega1280/2560 support by Brett Hagman (http://www.roguerobotics.com/)
This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
Lesser General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
License along with this library; if not, write to the Free Software
Foundation, Inc., 51 Franklin St, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA
The latest version of this library can always be found at
http://arduiniana.org.
*/
// When set, _DEBUG co-opts pins 11 and 13 for debugging with an
// oscilloscope or logic analyzer. Beware: it also slightly modifies
// the bit times, so don't rely on it too much at high baud rates
#define _DEBUG 0
#define _DEBUG_PIN1 11
#define _DEBUG_PIN2 13
//
// Includes
//
#include <avr/interrupt.h>
#include <avr/pgmspace.h>
#include <Arduino.h>
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
#include <util/delay_basic.h>
extern alert();
//
// Statics
//
SoftwareSerial *SoftwareSerial::active_object = 0;
char SoftwareSerial::_receive_buffer[_SS_MAX_RX_BUFF];
volatile uint8_t SoftwareSerial::_receive_buffer_tail = 0;
volatile uint8_t SoftwareSerial::_receive_buffer_head = 0;
//
// Debugging
//
// This function generates a brief pulse
// for debugging or measuring on an oscilloscope.
inline void DebugPulse(uint8_t pin, uint8_t count)
{
#if _DEBUG
volatile uint8_t *pport = portOutputRegister(digitalPinToPort(pin));
uint8_t val = *pport;
while (count--)
{
*pport = val | digitalPinToBitMask(pin);
*pport = val;
}
#endif
}
//
// Private methods
//
/* static */
inline void SoftwareSerial::tunedDelay(uint16_t delay) {
_delay_loop_2(delay);
}
// This function sets the current object as the "listening"
// one and returns true if it replaces another
bool SoftwareSerial::listen()
{
if (!_rx_delay_stopbit)
return false;
if (active_object != this)
{
if (active_object)
active_object->stopListening();
_buffer_overflow = false;
_receive_buffer_head = _receive_buffer_tail = 0;
active_object = this;
setRxIntMsk(true);
return true;
}
return false;
}
// Stop listening. Returns true if we were actually listening.
bool SoftwareSerial::stopListening()
{
if (active_object == this)
{
setRxIntMsk(false);
active_object = NULL;
return true;
}
return false;
}
//
// The receive routine called by the interrupt handler
//
void SoftwareSerial::recv()
{
#if GCC_VERSION < 40302
// Work-around for avr-gcc 4.3.0 OSX version bug
// Preserve the registers that the compiler misses
// (courtesy of Arduino forum user *etracer*)
asm volatile(
"push r18 \n\t"
"push r19 \n\t"
"push r20 \n\t"
"push r21 \n\t"
"push r22 \n\t"
"push r23 \n\t"
"push r26 \n\t"
"push r27 \n\t"
::);
#endif
uint8_t d = 0;
// If RX line is high, then we don't see any start bit
// so interrupt is probably not for us
if (_inverse_logic ? rx_pin_read() : !rx_pin_read())
{
// Disable further interrupts during reception, this prevents
// triggering another interrupt directly after we return, which can
// cause problems at higher baudrates.
setRxIntMsk(false);
// Wait approximately 1/2 of a bit width to "center" the sample
tunedDelay(_rx_delay_centering);
DebugPulse(_DEBUG_PIN2, 1);
// Read each of the 8 bits
for (uint8_t i=8; i > 0; --i)
{
tunedDelay(_rx_delay_intrabit);
d >>= 1;
DebugPulse(_DEBUG_PIN2, 1);
if (rx_pin_read())
d |= 0x80;
}
if (_inverse_logic)
d = ~d;
// if buffer full, set the overflow flag and return
uint8_t next = (_receive_buffer_tail + 1) % _SS_MAX_RX_BUFF;
if (next != _receive_buffer_head)
{
// save new data in buffer: tail points to where byte goes
_receive_buffer[_receive_buffer_tail] = d; // save new byte
_receive_buffer_tail = next;
}
else
{
DebugPulse(_DEBUG_PIN1, 1);
_buffer_overflow = true;
}
// skip the stop bit
tunedDelay(_rx_delay_stopbit);
DebugPulse(_DEBUG_PIN1, 1);
// Re-enable interrupts when we're sure to be inside the stop bit
setRxIntMsk(true);
}
#if GCC_VERSION < 40302
// Work-around for avr-gcc 4.3.0 OSX version bug
// Restore the registers that the compiler misses
asm volatile(
"pop r27 \n\t"
"pop r26 \n\t"
"pop r23 \n\t"
"pop r22 \n\t"
"pop r21 \n\t"
"pop r20 \n\t"
"pop r19 \n\t"
"pop r18 \n\t"
::);
#endif
}
uint8_t SoftwareSerial::rx_pin_read()
{
return *_receivePortRegister & _receiveBitMask;
}
//
// Interrupt handling
//
/* static */
inline void SoftwareSerial::handle_interrupt()
{
if (active_object)
{
active_object->recv();
}
}
#if defined(PCINT0_vect)
ISR(PCINT0_vect)
{
alert();
SoftwareSerial::handle_interrupt();
}
#endif
#if defined(PCINT1_vect)
ISR(PCINT1_vect, ISR_ALIASOF(PCINT0_vect));
#endif
#if defined(PCINT2_vect)
ISR(PCINT2_vect, ISR_ALIASOF(PCINT0_vect));
#endif
#if defined(PCINT3_vect)
ISR(PCINT3_vect, ISR_ALIASOF(PCINT0_vect));
#endif
//
// Constructor
//
SoftwareSerial::SoftwareSerial(uint8_t receivePin, uint8_t transmitPin, bool inverse_logic /* = false */) :
_rx_delay_centering(0),
_rx_delay_intrabit(0),
_rx_delay_stopbit(0),
_tx_delay(0),
_buffer_overflow(false),
_inverse_logic(inverse_logic)
{
setTX(transmitPin);
setRX(receivePin);
}
//
// Destructor
//
SoftwareSerial::~SoftwareSerial()
{
end();
}
void SoftwareSerial::setTX(uint8_t tx)
{
// First write, then set output. If we do this the other way around,
// the pin would be output low for a short while before switching to
// output hihg. Now, it is input with pullup for a short while, which
// is fine. With inverse logic, either order is fine.
digitalWrite(tx, _inverse_logic ? LOW : HIGH);
pinMode(tx, OUTPUT);
_transmitBitMask = digitalPinToBitMask(tx);
uint8_t port = digitalPinToPort(tx);
_transmitPortRegister = portOutputRegister(port);
}
void SoftwareSerial::setRX(uint8_t rx)
{
pinMode(rx, INPUT);
if (!_inverse_logic)
digitalWrite(rx, HIGH); // pullup for normal logic!
_receivePin = rx;
_receiveBitMask = digitalPinToBitMask(rx);
uint8_t port = digitalPinToPort(rx);
_receivePortRegister = portInputRegister(port);
}
uint16_t SoftwareSerial::subtract_cap(uint16_t num, uint16_t sub) {
if (num > sub)
return num - sub;
else
return 1;
}
//
// Public methods
//
void SoftwareSerial::begin(long speed)
{
_rx_delay_centering = _rx_delay_intrabit = _rx_delay_stopbit = _tx_delay = 0;
// Precalculate the various delays, in number of 4-cycle delays
uint16_t bit_delay = (F_CPU / speed) / 4;
// 12 (gcc 4.8.2) or 13 (gcc 4.3.2) cycles from start bit to first bit,
// 15 (gcc 4.8.2) or 16 (gcc 4.3.2) cycles between bits,
// 12 (gcc 4.8.2) or 14 (gcc 4.3.2) cycles from last bit to stop bit
// These are all close enough to just use 15 cycles, since the inter-bit
// timings are the most critical (deviations stack 8 times)
_tx_delay = subtract_cap(bit_delay, 15 / 4);
// Only setup rx when we have a valid PCINT for this pin
if (digitalPinToPCICR(_receivePin)) {
#if GCC_VERSION > 40800
// Timings counted from gcc 4.8.2 output. This works up to 115200 on
// 16Mhz and 57600 on 8Mhz.
//
// When the start bit occurs, there are 3 or 4 cycles before the
// interrupt flag is set, 4 cycles before the PC is set to the right
// interrupt vector address and the old PC is pushed on the stack,
// and then 75 cycles of instructions (including the RJMP in the
// ISR vector table) until the first delay. After the delay, there
// are 17 more cycles until the pin value is read (excluding the
// delay in the loop).
// We want to have a total delay of 1.5 bit time. Inside the loop,
// we already wait for 1 bit time - 23 cycles, so here we wait for
// 0.5 bit time - (71 + 18 - 22) cycles.
_rx_delay_centering = subtract_cap(bit_delay / 2, (4 + 4 + 75 + 17 - 23) / 4);
// There are 23 cycles in each loop iteration (excluding the delay)
_rx_delay_intrabit = subtract_cap(bit_delay, 23 / 4);
// There are 37 cycles from the last bit read to the start of
// stopbit delay and 11 cycles from the delay until the interrupt
// mask is enabled again (which _must_ happen during the stopbit).
// This delay aims at 3/4 of a bit time, meaning the end of the
// delay will be at 1/4th of the stopbit. This allows some extra
// time for ISR cleanup, which makes 115200 baud at 16Mhz work more
// reliably
_rx_delay_stopbit = subtract_cap(bit_delay * 3 / 4, (37 + 11) / 4);
#else // Timings counted from gcc 4.3.2 output
// Note that this code is a _lot_ slower, mostly due to bad register
// allocation choices of gcc. This works up to 57600 on 16Mhz and
// 38400 on 8Mhz.
_rx_delay_centering = subtract_cap(bit_delay / 2, (4 + 4 + 97 + 29 - 11) / 4);
_rx_delay_intrabit = subtract_cap(bit_delay, 11 / 4);
_rx_delay_stopbit = subtract_cap(bit_delay * 3 / 4, (44 + 17) / 4);
#endif
// Enable the PCINT for the entire port here, but never disable it
// (others might also need it, so we disable the interrupt by using
// the per-pin PCMSK register).
*digitalPinToPCICR(_receivePin) |= _BV(digitalPinToPCICRbit(_receivePin));
// Precalculate the pcint mask register and value, so setRxIntMask
// can be used inside the ISR without costing too much time.
_pcint_maskreg = digitalPinToPCMSK(_receivePin);
_pcint_maskvalue = _BV(digitalPinToPCMSKbit(_receivePin));
tunedDelay(_tx_delay); // if we were low this establishes the end
}
#if _DEBUG
pinMode(_DEBUG_PIN1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(_DEBUG_PIN2, OUTPUT);
#endif
listen();
}
void SoftwareSerial::setRxIntMsk(bool enable)
{
if (enable)
*_pcint_maskreg |= _pcint_maskvalue;
else
*_pcint_maskreg &= ~_pcint_maskvalue;
}
void SoftwareSerial::end()
{
stopListening();
}
// Read data from buffer
int SoftwareSerial::read()
{
if (!isListening())
return -1;
// Empty buffer?
if (_receive_buffer_head == _receive_buffer_tail)
return -1;
// Read from "head"
uint8_t d = _receive_buffer[_receive_buffer_head]; // grab next byte
_receive_buffer_head = (_receive_buffer_head + 1) % _SS_MAX_RX_BUFF;
return d;
}
int SoftwareSerial::available()
{
if (!isListening())
return 0;
return (_receive_buffer_tail + _SS_MAX_RX_BUFF - _receive_buffer_head) % _SS_MAX_RX_BUFF;
}
size_t SoftwareSerial::write(uint8_t b)
{
if (_tx_delay == 0) {
setWriteError();
return 0;
}
// By declaring these as local variables, the compiler will put them
// in registers _before_ disabling interrupts and entering the
// critical timing sections below, which makes it a lot easier to
// verify the cycle timings
volatile uint8_t *reg = _transmitPortRegister;
uint8_t reg_mask = _transmitBitMask;
uint8_t inv_mask = ~_transmitBitMask;
uint8_t oldSREG = SREG;
bool inv = _inverse_logic;
uint16_t delay = _tx_delay;
if (inv)
b = ~b;
cli(); // turn off interrupts for a clean txmit
// Write the start bit
if (inv)
*reg |= reg_mask;
else
*reg &= inv_mask;
tunedDelay(delay);
// Write each of the 8 bits
for (uint8_t i = 8; i > 0; --i)
{
if (b & 1) // choose bit
*reg |= reg_mask; // send 1
else
*reg &= inv_mask; // send 0
tunedDelay(delay);
b >>= 1;
}
// restore pin to natural state
if (inv)
*reg &= inv_mask;
else
*reg |= reg_mask;
SREG = oldSREG; // turn interrupts back on
tunedDelay(_tx_delay);
return 1;
}
void SoftwareSerial::flush()
{
if (!isListening())
return;
uint8_t oldSREG = SREG;
cli();
_receive_buffer_head = _receive_buffer_tail = 0;
SREG = oldSREG;
}
int SoftwareSerial::peek()
{
if (!isListening())
return -1;
// Empty buffer?
if (_receive_buffer_head == _receive_buffer_tail)
return -1;
// Read from "head"
return _receive_buffer[_receive_buffer_head];
}
![]()